
Do you experience blurry or distorted vision, especially at night? Do streetlights or headlights appear streaky or haloed? If so, you may have astigmatism, a prevalent vision issue that influences the clarity of the image you see.
Unlike nearsightedness or farsightedness, which impact vision at specific distances, astigmatism affects clarity at all distances.
A Study by NIH indicates that approximately 36.2% of individuals experience astigmatism. Its prevalence increases with age, rising from 14.3% in individuals under 15 to 67.2% in those over 65.
This condition arises from an irregular shape of the cornea or lens that hinders proper light focus on the retina. While people with normal vision experience sharp and crisp eyesight, those with astigmatism often see streaks, glare, and shadows around objects. But what exactly does astigmatism look like compared to normal vision?
In this guide, we will compare astigmatism to normal vision and compare how lights appear with and without astigmatism. Lastly, we will also discuss its causes and symptoms and treatment options that can help restore clarity.
What Is Normal Vision?
A healthy eye processes light effectively to create a clear image of both near and distant objects. In normal vision, the cornea and lens are evenly curved, ensuring that light rays focus directly on the retina. This precise focus allows the brain to interpret clear, detailed images without distortion. With normal vision, you can easily read text, recognise faces, and see clearly at any distance.
What Is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism is a refractive error where the cornea or lens resembles a football shape rather than a basketball. This irregular curvature prevents light rays from converging at one point on the retina and causes blurred and distorted vision.
Types of Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a prevalent vision condition, but did you know it has various types? The way light refracts as it enters your eye relies on the shape of your cornea and lens. Let’s simplify this explanation.
Corneal vs. Lenticular Astigmatism
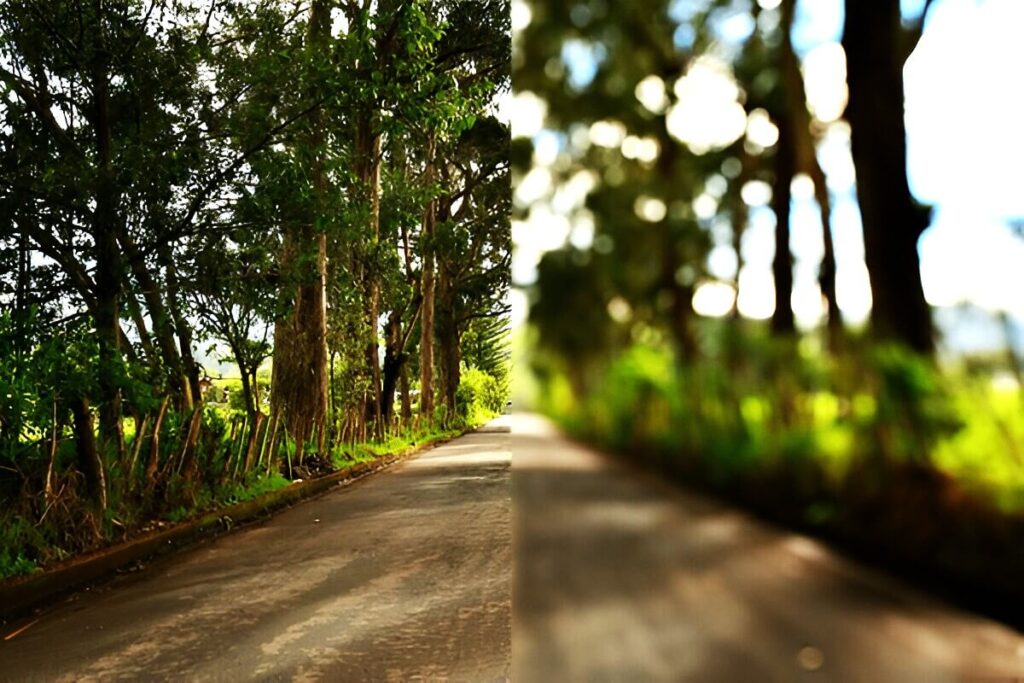

Astigmatism arises when your eye fails to focus light uniformly, resulting in blurry or distorted vision. This condition is caused by irregularities in the cornea or the eye’s lens.
- Corneal astigmatism happens when your cornea has an oval or irregular shape instead of being perfectly round. This irregular surface distorts light, leading to vision problems.
- Lenticular astigmatism happens due to an uneven curvature of the lens in the eye, which impacts light focus on the retina.
Types of Astigmatism: On the Base of the Shape of Cornea
The way your cornea curves can also determine the type of astigmatism you have. Here are the three main types:
- With-the-Rule Astigmatism: This is the most common type, where the cornea is steeper vertically (like a football standing upright).
- Against-the-Rule Astigmatism: In this case, the cornea is more horizontally curved (similar to a football resting on its side).
- Oblique Astigmatism: Instead of being steeper vertically or horizontally, the cornea’s curvature is tilted at an angle. That makes the light focus in an unusual way.
How Does Astigmatism Affect Vision?

Astigmatism affects your vision by causing objects to appear distorted, whether they are near or far. This condition can make tasks like driving, reading, and recognizing faces more difficult by impacting clarity and depth perception.
Astigmatism vs Normal Vision
Unlike normal vision, which allows you to see sharp and clear images at all distances, astigmatism causes blurred vision regardless of how far away an object is. Moreover, you might see elongated, duplicated, or shadowy objects, which can obscure fine details.
Individuals with astigmatism often suffer from persistent headaches and eye strain as their eyes exert extra effort to adjust for uneven focus.
Astigmatism Lights vs Normal Vision
A significant frustration of astigmatism is its impact on light perception. You may notice halos, streaks, or smudges around bright objects. This makes focusing on illuminated signs, screens, or car headlights difficult.
Visual distortions can pose significant distractions when using digital devices or operating a vehicle at night. Headlights and streetlights may appear excessively bright and scattered, increasing discomfort and reducing visibility.
Astigmatism at Night vs Normal Vision
Night driving can be challenging and even hazardous for you if you have astigmatism. Oncoming headlights produce intense glare and make it difficult to focus on the road. Street signs and lane markers may appear blurry.
Studies showcase that astigmatism can cause reduced contrast sensitivity that leads to difficulties in tasks such as night driving. Uncorrected astigmatism significantly impairs night driving performance and the risk of accidents.
Additionally, depth perception becomes less accurate which makes it harder to judge distances between vehicles, curbs, or intersections.
These vision issues make it hard to see in low light, which can make navigation in the dark stressful. Many people need glasses or other visual aids to improve clarity and stay safe.
What Causes Astigmatism?
Astigmatism often runs in families, but several factors can contribute to its development:
- Genetics: The most common cause; many people are born with it.
- Eye Injuries or Surgeries: Trauma or procedures can change the cornea’s shape.
- Keratoconus: A progressive eye disease that causes the cornea to thin and bulge.
- Environmental Factors: Eye strain and excessive rubbing may contribute to worsening astigmatism.
What Are the Symptoms of Astigmatism?
If you struggle to see clearly or often squint, astigmatism could be the reason. Let’s explore the most common symptoms of astigmatism. It will help to diagnose and treat it on time.
- Blurry vision at all distances.
- Difficulty focusing on text or small details.
- Astigmatism causes lights at night to appear as halos and glare.
- Frequent headaches or eye discomfort.
- Squinting to see more clearly.
How Is Astigmatism Diagnosed?
Eye care professionals use several tests to detect astigmatism and assess its severity. We have picked the most commonly used tests mentioned below.
1. Visual Acuity Test
In this test, your doctor asks you to read letters from a chart at different distances. This helps them measure how clearly you can see and identify any vision impairments.
2. Keratometry
A specialised device measures the curvature of your cornea to determine how much your eye shape affects light refraction.
3. Corneal Topography
Corneal topography, an advanced imaging test, creates a detailed map of your cornea’s surface. It detects irregularities that contribute to astigmatism and other vision issues.
3 Best Options for Correcting Astigmatism
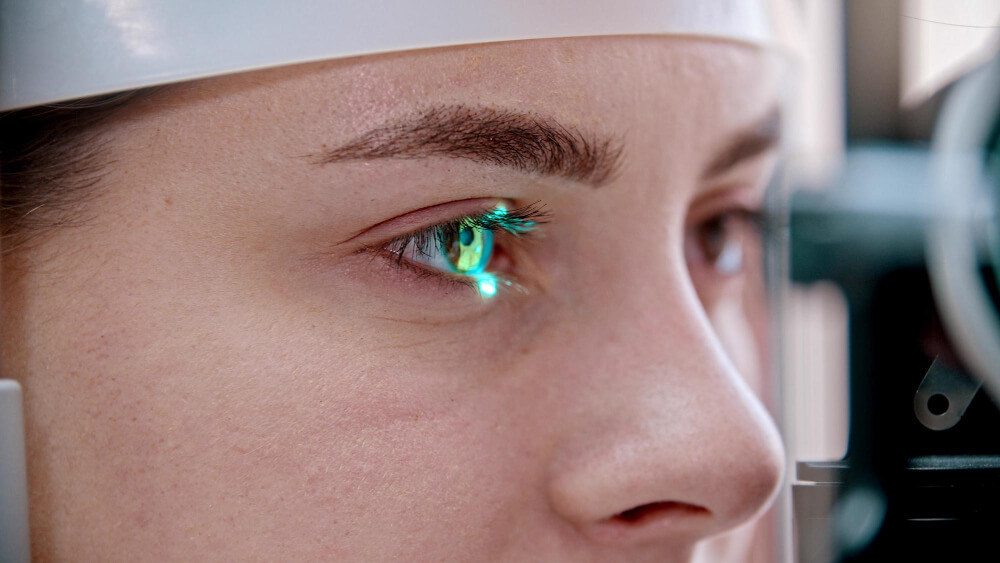
Astigmatism can make daily tasks difficult, but the right correction can restore clear vision. Whether you prefer glasses, contact lenses, or a more permanent solution, there are effective ways to manage astigmatism.
1. Eyeglasses and Contact Lenses
Wearing glasses is the most common and easiest way to correct astigmatism. They adjust how light enters the eye, ensuring clearer vision at all distances.
Toric contact lenses are another option. They are designed to align with the shape of an astigmatic eye. They provide sharper vision compared to standard lenses and are ideal for individuals with astigmatism.
2. Orthokeratology (Ortho-K)
Ortho-K uses special rigid contact lenses that reshape the cornea while you sleep. This temporary correction allows clear vision during the day without needing glasses or contacts.
It works best for mild to moderate astigmatism and is a good alternative for those who are not ready for surgery.
3. Refractive Surgery
For a long-term solution, refractive surgeries like LASIK, PRK, and LASEK permanently reshape the cornea. These procedures improve how light focuses on the retina, reducing or eliminating the need for corrective lenses. Surgery is ideal for eligible candidates seeking lasting vision improvement.
Texan Eye Care: Your Trusted Eye Health Partner
With 25 years of experience in eye care, Texan Eye understands how astigmatism impacts daily life. Our internationally known and expert ophthalmologists and optometrists have worked in the field for years. They know how to use advanced diagnostic tools and provide comprehensive eye exams and personalised vision solutions.
Moreover, our hygienic environment, easy process, and caring and kind staff make it an ideal experience for our patients. Whether you need custom-fitted toric lenses, Ortho-K, or LASIK surgery, we tailor treatments to match your convenience and lifestyle.
Wrap Up
We wrap up our discussion by saying that astigmatism affects how you see the world. Blurry vision, glare, and night driving difficulties can make daily life frustrating. But the good news is that effective treatments are available.
Eyeglasses and contact lenses offer quick and simple correction. Ortho-K provides a temporary, lens-free solution. For a permanent fix, refractive surgery reshapes the cornea to restore clear vision. The right choice depends on your lifestyle, preferences, and eye health.
At Texan Eye, we provide expert eye exams, customised vision correction, and advanced treatment options for astigmatism. Whether you need glasses, contacts, or surgery, our specialists will help you find the best solution for your vision needs.
